Список флагов округов Германии
This article is missing information about the details of the flags. (August 2023) |
This article needs additional citations for verification. (July 2024) |
Это список флагов округов Германии . Флаги перечислены по землям . Большинство округов Германии имеют как горизонтальные, так и вертикальные флаги. На этих флагах обычно были гербы. Поэтому в списке также будет обсуждаться герб. Обратите внимание, что некоторые из перечисленных флагов либо являются флагами де-факто , либо еще не утверждены.
| Флаг | Округ | Дата | Описание |
|---|---|---|---|
 | Баден-Баден | 1421 – настоящее время | Желто-красно-желтый горизонтальный флаг с гербом. [1] |
 | Фрайбург-им-Брайсгау | 1368 – настоящее время | Флаг с Георгиевским крестом |
 | Гейдельберг | 1938 – настоящее время | Черно-желтый горизонтальный биколор. |
 | Хайльбронн (городской округ) | 19 век – настоящее время | Красно-бело-синий горизонтальный триколор. [2] |
 | Карлсруэ (городской округ) | 1895 – настоящее время | Красно-желто-красный горизонтальный флаг. |
 | Мангейм | 1613 – настоящее время | Сине-бело-красный горизонтальный триколор. |
 | 1896 – настоящее время | Вертикальный флаг с гербом. Герб состоит из Пфальцского льва, представляющего Мангейм как последнюю столицу Курпфальца , и Вольфсангеля, представляющего границы. [3] | |
 | Офтердинген | 6 июня 1982 г. – настоящее время | Желто-голубой горизонтальный биколор с гербом. [4] |
 | Пфорцхайм | 18 век – настоящее время | Бело-голубой горизонтальный биколор с гербом. Дестер представляет Баден. Желтый также представляет Баден, а белый и синий, как говорят, происходят от дома Виттельсбахов. |
 | Штутгарт | 1950 – настоящее время | Черно-желтый горизонтальный биколор с гербом. Герб является отсылкой к легенде, в которой Людольф, герцог Швабии, основал ранчо, коневодческий центр и школу верховой езды на месте, где сейчас находится город. |
 | Вертикальный флаг. | ||
 | Ульм | 1244 – настоящее время | Черно-белый горизонтальный биколор. Значение цветов до сих пор неизвестно. [5] |
- Флаг Альб-Донау-Крайс
- Флаг Бибераха
- Флаг Бодензеекрейса
- Флаг Бодензекрайса (вариант)
- Флаг Бёблингена
- Флаг Кальва
- Флаг Эммендингена
- Флаг Энцкрейса
- Флаг Эсслингена
- Флаг Фройденштадта
- Флаг Гёппингена
- Флаг Гейдельберга
- Флаг Хайденхайма
- Флаг Хайльбронна (округ)
- Флаг Гогенлоэ
- Флаг Карлсруэ (земельный округ)
- Флаг Констанца
- Флаг Лёрраха
- Флаг Людвигсбурга
- Флаг округа Майн-Таубер
- Флаг округа Неккар-Оденвальд
- Флаг Ортенаукрайса
- Флаг Восточного округа
- Флаг Раштатта
- Флаг Равенсбурга
- Флаг округа Ремс-Мурр
- Флаг Ройтлингена
- Флаг округа Рейн-Неккар
- Флаг Ротвайля
- Флаг Швебиш-Халля
- Флаг Зигмарингена
- Флаг Тюбингена
- Флаг Вальдсхута
- Флаг округа Цоллернальбкрайс
| Флаг | Округ | Дата | Описание |
|---|---|---|---|
 | Ландсхут | 23 мая 1973 г. (де-факто) – | Белый флаг, два ряда синих ромбов слева и справа, герб. |
 | 23 мая 1973 г. – | Бело-голубой горизонтальный флаг с гербом. | |
 | Айхах-Фридберг | 1 января 1973 г. – | Зелено-желтый горизонтальный флаг с гербом. |
- Флаг Амберга
- Флаг Альтёттинга
- Флаг Амберг-Зульцбаха
- Флаг Ансбаха (земельный округ)
- Флаг Ансбаха (городской округ)
- Флаг Ашаффенбурга (Ландкрайс)
- Флаг Ашаффенбурга (Stadtkreis)
- Флаг Аугсбурга (земельный округ)
- Флаг Аугсбурга (городской округ)
- Флаг Бад-Киссингена
- Флаг Бамберга (земельный округ)
- Флаг Бамберга (городской округ)
- Флаг Байройта (земельного округа)
- Флаг Байройта (городской округ)
- Флаг земли Берхтесгаден
- Флаг Чама
- Флаг Кобурга (земельного округа)
- Флаг Кобурга (Stadtkreis)
- Флаг Дахау
- Флаг Деггендорфа
- Флаг Диллингена
- Флаг Дингольфинга-Ландау
- Флаг Донау-Риса
- Флаг Эберсберга
- Флаг Айхштетта
- Флаг Эрдинга
- Флаг Эрлангена
- Флаг Эрланген-Хёхштадта
- Флаг Форххайма
- Флаг Фрайзинга
- Флаг Фрайунг-Графенау
- Флаг Фюрстенфельдбрука
- Флаг Фюрта (городской округ)
- Флаг Фюрта (земельного округа)
- Флаг Гармиш-Партенкирхена
- Флаг Гюнцбурга
- Флаг Хассберге
- Флаг Хофа (земельного округа)
- Флаг Ингольштадта
- Флаг Кауфбойрена
- Флаг Кельхайма
- Флаг Кемптена
- Флаг Китцингена
- Флаг Кронаха
- Флаг Кульмбаха
- Флаг Ландсберга
- Флаг Ландсхута (городской округ)
- Флаг Лихтенфельса
- Флаг Линдау
- Флаг Майн-Шпессарта
- Флаг Меммингена
- Флаг Мисбаха
- Флаг Мильтенберга
- Флаг Мюльдорфа
- Флаг Мюнхена (Landkreis)
- Флаг Мюнхена (Stadtkreis; полосатый вариант)
- Флаг Мюнхена (Stadtkreis; ромбический вариант)
- Флаг Ноймаркта
- Флаг Ной-Ульма
- Флаг Нюрнберга
- Флаг Нюрнбергской земли
- Флаг Верхнего Альгоя
- Флаг Восточного Альгоя
- Флаг Пассау (земельный округ)
- Флаг Пассау (городской округ)
- Флаг Пфаффенхофена
- Флаг Регена
- Флаг Регенсбурга (Landkreis)
- Флаг Регенсбурга (Stadtkreis)
- Флаг Рён-Грабфельда
- Флаг Розенхайма (земельный округ)
- Флаг Розенхайма (Stadtkreis)
- Флаг Рота
- Флаг Роттал-Инна
- Флаг Швабаха
- Флаг Швандорфа
- Флаг Швайнфурта (Ландкрайс)
- Флаг Швайнфурта (Stadtkreis)
- Флаг Штарнберга
- Флаг Штраубинга
- Флаг Штраубинг-Боген
- Флаг Тиршенройта
- Флаг Траунштайна
- Флаг Унтеральгой
- Флаг Вайльхайм-Шонгау
- Флаг Вунзиделя
- Флаг Вюрцбурга (земельный округ)
- Флаг Вюрцбурга (Stadtkreis)
- Флаг Барнима
- Флаг Котбуса
- Флаг Даме-Шпревальда
- Флаг Эльбы-Эльстера
- Флаг Франкфурта (Одер)
- Флаг Хафельланда
- Флаг Меркиш-Одерланда
- Флаг Оберхафеля
- Флаг Обершпревальд-Лаузиц
- Флаг Одер-Шпрее
- Флаг Остпригниц-Руппин
- Флаг Потсдама
- Флаг Пригница
- Флаг Шпрее-Нейсе
- Флаг Тельтов-Флеминга
- Флаг Укермарка
| Флаг | Округ | Дата | Описание |
|---|---|---|---|
 | Берлин | 26 мая 1954 г. – | Красно-бело-красный флаг с черным медведем. |
| Флаг | Округ | Дата | Описание |
|---|---|---|---|
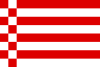 | Бремен | 1952 – | Флаг представляет собой восемь равных горизонтальных полос красного и белого цветов, расположенных у древка. |
 | Вариант с гербом. | ||
 | Вариант с большим гербом. |
| Флаг | Округ | Дата | Описание |
|---|---|---|---|
 | Гамбург | 1834 – | Красный флаг с белым замком. |
- Флаг Бергштрассе
- Флаг Дармштадта
- Флаг Дармштадта-Дибурга
- Флаг Франкфурта
- Флаг Фульды
- Флаг Гиссена
- Флаг Гросс-Герау
- Флаг Херсфельд-Ротенбурга
- Флаг Верхнего Таунуса
- Флаг Касселя (земельного округа)
- Флаг Касселя (Stadtkreis)
- Флаг округа Лан-Дилль
- Флаг Лимбург-Вайльбурга
- Флаг округа Майн-Кинциг
- Флаг округа Майн-Таунус
- Флаг Марбург-Биденкопф
- Флаг Оденвальдкрейса
- Флаг Оффенбаха
- Флаг Оффенбаха-на-Майне
- Флаг округа Рейнгау-Таунус
- Флаг округа Швальм-Эдер
- Флаг округа Фогельсберг
- Флаг Вальдек-Франкенберга
- Флаг округа Верра-Майснер
- Флаг Веттераукрайса
Исторический
- Флаг Биденкопфа (1959-1974 гг.)
- Флаг Биденкопфа (1959-1974; вариант)
- Флаг Бюдингена (1952-1972)
- Флаг Бюдингена (1952-1972; вариант)
- Флаг Дармштадта (1962-1976)
- Флаг Дармштадта (1962-1976; вариант)
- Флаг Дибурга (1961-1976)
- Флаг Дибурга (1961-1976; вариант)
- Флаг Лаутербаха (1964-1974)
- Флаг Лаутербаха (1964–1974; вариант)
- Флаг Шлюхтерна (1956-1974)
- Флаг Шлюхтерна (1956–1974; вариант)
- Флаг Вальдека (1955-1974)
- Флаг Вальдека (1955-1974; вариант)
- Флаг Аммерланда
- Флаг Ауриха
- Флаг графства Бентхайм
- Флаг Брауншвейга
- Флаг Целле
- Флаг Клоппенбурга
- Флаг Куксхафена
- Флаг Дельменхорста
- Флаг Дипхольца
- Флаг Эмдена
- Флаг Эмсланда
- Флаг Фрисландии
- Флаг Фрисландии (вариант)
- Флаг Гифхорна
- Флаг Гослара
- Флаг Гёттингена
- Флаг Гёттингена (вариант)
- Флаг Хамельн-Пирмонта
- Флаг Хамельн-Пирмонта (вариант)
- Флаг региона Ганновер
- Флаг Харбурга
- Флаг Хайдекрайс
- Флаг Хельмштедта
- Флаг Хольцминдена
- Флаг Леера
- Флаг Люхов-Данненберга
- Флаг Люнебурга
- Флаг Нинбурга
- Флаг Нортхайма
- Флаг Ольденбурга (земельного округа)
- Флаг Ольденбурга (Stadtkreis)
- Флаг Оснабрюка (Landkreis)
- Флаг Оснабрюка (Stadtkreis)
- Флаг Остерхольца
- Флаг Пайне
- Флаг Ротенбурга
- Флаг Зальцгиттера
- Флаг Шаумбурга
- Флаг Штаде
- Флаг Ильцена
- Флаг Фехты
- Флаг Вердена
- Флаг Везермарша
- Флаг Вильгельмсхафена
- Флаг Виттмунда
- Флаг Вольфенбюттеля
- Флаг Вольфсбурга
Исторический
- Флаг Гёттингена (1973–2017)
- Флаг Гёттингена (1973–2017; вариант)
| Флаг | Округ | Дата | Описание |
|---|---|---|---|
 | Людвигслуст-Пархим | 27 января 2015 г. – | Знамя герба. Серая цапля на синем фоне символизирует природу, воду и биоразнообразие, голова коронованного быка на желтом фоне символизирует Мекленбург и Пархим, а ветвь дуба символизирует Людвигслуст . Дизайн Хайнца Киппника. [6] |
 | Мекленбургское поозёрье | 11 марта 2014 г. – | Сине-желтый флаг с гербом. Красный грифон представляет герцогство Померания , а голова быка представляет Верле . Сине-белые волны представляют водоемы. Общее количество волн представляет Альтентрептов , Деммин , Нойбранденбург , Нойштрелиц , Мальхин , Варен и Рёбель . Дизайн Хайнца Киппника. [7] |
 | Нордвестмекленбург | 15 февраля 2012 г. – | Знамя герба. Голова быка на желтом фоне представляет герцогство Мекленбург-Шверин , а посох на красно-белых полосах представляет . Красный и белый были цветами Ганзейского союза . Разработан Манфредом Гертом. [8] [9] |
 | Росток (округ) | 15 ноября 2011 г. – | Banner of arms. The bull's head on yellow represents Lordship of Werle and the griffin's head represents the Lordship of Rostock. Two crossed crosiers symbolizes Doberan Abbey. Designed by Manfred Gerth.[10] |
 | Rostock (Stadtkreis) | 3 July 1991 – | Banner of arms. The yellow griffin represents the Lordship of Rostock. Blue, white and red are traditional colours of Mecklenburg-Vorpommern. White and red are colours of the Hanseatic League.[11] |
 | Schwerin | 1994 – | Yellow-blue-yellow flag with a knight in the middle blue stripe. The knight is a depiction of Henry the Lion.[12][13] |
 | Vorpommern-Greifswald | TBA | No official flag. |
 | Vorpommern-Rügen | 10 October 2013 – | Blue and yellow horizontal flag with the coat of arms. |
Historical
| Flag | District | Date | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
 | Bad Doberan | 1 August 1996 – 4 September 2011 | Yellow and blue horizontal flag. The yellow griffin represents Rostock, the bull's head represents the Werle and the crosier represents the Cistercians.[14] |
 | Demmin | 26 March 1996 – 4 September 2011 | Flag with seven blue, yellow and red stripes. |
 | Mueritz | 1995 – 4 September 2011 | |
 | Ostvorpommern | 1998 – 4 September 2011 | |
 | Parchim | 1995 – 4 September 2011 | |
 | Nordwestmecklenburg | 2006 – 4 September 2011 |
- Flag of Aachen
- Flag of Bielefeld
- Flag of Bielefeld (variant)
- Flag of Bochum
- Flag of Bochum (variant)
- Flag of Bonn
- Flag of Borken
- Flag of Borken (variant)
- Flag of Bottrop
- Flag of Bottrop (variant)
- Flag of Coesfeld
- Flag of Coesfeld (variant)
- Flag of Cologne
- Flag of Cologne (variant)
- Flag of Dortmund
- Flag of Dortmund (variant)
- Flag of Duisburg
- Flag of Duisburg (variant)
- Flag of Düren
- Flag of Düsseldorf
- Flag of Düsseldorf (variant)
- Flag of Ennepe-Ruhr-Kreis
- Flag of Ennepe-Ruhr-Kreis (variant 1)
- Flag of Ennepe-Ruhr-Kreis (variant 2)
- Flag of Essen
- Flag of Essen (variant)
- Flag of Euskirchen
- Flag of Euskirchen (variant)
- Flag of Gütersloh
- Flag of Gütersloh (variant)
- Flag of Hagen
- Flag of Hamm
- Flag of Hamm (variant)
- Flag of Heinsberg
- Flag of Heinsberg (variant)
- Flag of Herford
- Flag of Herford (variant)
- Flag of Herne
- Flag of Hochsauerlandkreis
- Flag of Hochsauerlandkreis (variant)
- Flag of Höxter
- Flag of Höxter (variant)
- Flag of Kleve
- Flag of Kleve (variant)
- Flag of Krefeld
- Flag of Krefeld (variant)
- Flag of Leverkusen
- Flag of Leverkusen (variant)
- Flag of Lippe
- Flag of Lippe (variant)
- Flag of Märkischer Kreis
- Flag of Mettmann
- Flag of Minden-Lübbecke
- Flag of Minden-Lübbecke (variant)
- Flag of Mönchengladbach
- Flag of Mönchengladbach (variant)
- Flag of Mülheim
- Flag of Mülheim (variant)
- Flag of Münster
- Flag of Münster (variant 1)
- Flag of Münster (variant 2)
- Flag of Oberbergischer Kreis
- Flag of Oberbergischer Kreis (variant)
- Flag of Oberhausen
- Flag of Oberhausen (variant)
- Flag of Olpe
- Flag of Olpe (variant)
- Flag of Paderborn
- Flag of Recklinghausen
- Flag of Recklinghausen (variant)
- Flag of Remscheid
- Flag of Remscheid (variant)
- Flag of Rhein-Erft-Kreis
- Flag of Rheinisch-Bergischer Kreis
- Flag of Rhein-Kreis Neuss
- Flag of Rhein-Kreis Neuss
- Flag of Rhein-Sieg-Kreis
- Flag of Siegen-Wittgenstein
- Flag of Siegen-Wittgenstein (variant)
- Flag of Soest
- Flag of Soest (variant)
- Flag of Solingen
- Flag of Solingen (variant)
- Flag of Steinfurt
- Flag of Unna
- Flag of Viersen
- Flag of Viersen (variant)
- Flag of Warendorf
- Flag of Warendorf (variant)
- Flag of Wesel
- Flag of Wesel (variant)
- Flag of Wuppertal
- Flag of Wuppertal (variant)
Historical
- Flag of Brilon (1957-1976)
- Flag of Tecklenburg (1934-1975)
- Flag of Tecklenburg (1934-1975; variant)
- Flag of Ahrweiler
- Flag of Altenkirchen
- Flag of Alzey-Worms
- Flag of Bad Dürkheim
- Flag of Bad Kreuznach
- Flag of Bernkastel-Wittlich
- Flag of Birkenfeld
- Flag of Bitburg-Pruem
- Flag of Cochem-Zell
- Flag of Donnersbergkreis
- Flag of Germersheim
- Flag of Kaiserslautern (Landkreis)
- Flag of Kaiserslautern (Stadtkreis)
- Flag of Koblenz
- Flag of Kusel
- Flag of Ludwigshafen
- Flag of Mainz-Bingen
- Flag of Mainz
- Flag of Mayen-Koblenz
- Flag of Neustadt an der Weinstraße
- Flag of Neuwied
- Flag of Pirmasens
- Flag of Rhein-Hunsrück-Kreis
- Flag of Rhein-Lahn-Kreis
- Flag of Rhein-Pfalz-Kreis
- Flag of Speyer
- Flag of Südliche Weinstraße
- Flag of Südwestpfalz
- Flag of Trier
- Flag of Trier-Saarburg
- Flag of Vulkaneifel
- Flag of Westerwaldkreis
- Flag of Worms
- Flag of Zweibrücken
| Flag | Districf | Date | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
 | Merzig-Wadern | 1 February 1966 – | A red and yellow bicoloured flag with the coat of arms. |
 | Neunkirchen | 22 August 1961 – | A blue and white bicoloured flag with the coat of arms. |
 | Saarbrücken | 17 March 1975 – | A blue and yellow bicoloured flag with the coat of arms. |
 | Saarlouis | 1 February 1966 – | A black-red-yellow tricoloured flag with the coat of arms. |
 | Saarpfalz-Kreis | 21 May 1975 – | A white and blue bicoloured flag with the coat of arms. |
 | Sankt Wendel | 25 February 1965 – | A red and yellow bicoloured flag with the coat of arms. |
| Flag | Districf | Date | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
 | Bautzen | 2000 – | A blue-yellow flag with the coat of arms. |
 | Chemnitz | 1475 – | A blue-yellow flag. The colours are from the Margraviate of Landsberg.[15] |
 | Dresden | 1994 – | A black-yellow flag with the coat of arms. |
 | Erzgebirgskreis | 18 December 2008 – | A green-white flag with the coat of arms. |
 | Görlitz | 21 April 2009 – | A yellow-blue flag with the coat of arms. |
 | Leipzig (Landkreis) | 30 October 2009 (de facto) – | A white flag with the coat of arms. The blue and white wavy lines represents the Neuseenland, the yellow castle represents the Gnandstein Castle and the white gullet and three flowers represent Muldentalkreis.[16] |
 | Leipzig (Stadtkreis) | 1475 – | A blue-yellow flag with the coat of arms. The coat of arms consists of the Meissen lion on the left (representing the House of Wettin) and blue and yellow striped Landsberger Pfähle (representing the Margraviate of Landsberg).[17][18] |
 | Meissen | 27 April 2009 – | A yellow flag with the coat of arms in the centre with two red lines on left and right. |
 | Mittelsachsen | 27 April 2009 – | A black-yellow with the coat of arms. |
 | Nordsachsen | 10 December 2008 – | A yellow-blue-yellow with the coat of arms. |
 | Vogtlandkreis | 31 March 1996 – | A yellow-black with the coat of arms. |
 | Sächsische Schweiz-Osterzgebirge | TBA | No official flag. |
 | Zwickau | 4 December 2009 – | A red-white with the coat of arms. |
- Flag of Altmarkkreis Salzwedel
- Flag of Anhalt-Bitterfeld
- Flag of Börde
- Flag of Burgenlandkreis
- Flag of Dessau-Roßlau
- Flag of Halle (Saale)
- Flag of Harz
- Flag of Jerichower Land
- Flag of Magdeburg
- Flag of Mansfeld-Südharz
- Flag of Saalekreis
- Flag of Salzlandkreis
- Flag of Stendal
- Flag of Wittenberg
| Flag | City | Date | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
 | Dithmarschen | 17 May 1972 – | A white flag with 7 red and white stripes and the coat of arms. The coat of arms features a knight in gold armor riding a white horse. It represents its readiness for warfare. Designed by Wilhelm Horst Lippert.[19][20] |
 | Flensburg | 30 June 1938 – | A blue flag with the coat of arms. The two blue lions represents the Duchy of Schleswig, the silver nettle leaf in the red shield represents the Duchy of Holstein. The red tower represents the defense of the city. The waves represents the city's connection to the North Sea. Designed by Johannes Holtz, Max Kirmis, Erwin Nöbbe and Heinrich Sauermann.[21][22][23] |
 | Vertical variant. | ||
 | Herzogtum Lauenburg | 1948 – | A flag with two black stripes and the coat of arms. The coat of arms features a horse head represents Kingdom of Hanover and Denmark. The colours are from Prussia.[24][25] |
 | Kiel | 1921 – | A red flag based on the County of Schaumburg with a black boat representing the city's importance as a port inside a nesselblatt.[26] |
 | Vertical variant. | ||
 | Lübeck | 22 January 1941 – | White-red bicolor with a black eagle the Lübeck double eagle.[27] |
 | Vertical variant. | ||
 | Nordfriesland | 10 July 1972 – | Five horizontal bands of blue, yellow, and red (double width), with three ships to the left. The ships represents Eiderstedt, Everschop and Utholm. The sails of the ships contain a plough (representing Husum), a fish (representing Westerland as it is close to the sea) and a ox's head (representing Eiderstedt as it is known for its livestock). The colors were traditional colors of North Frisia. Designed by Wilhelm Horst Lippert.[28][29] |
 | Neumünster | 13 March 1930 – | White-red bicolor with the coat of arms. The coat of arms consists of a swan (representing Stormarn), a nesselblatt (representing Holstein) and five chimeys representing Neumünster. The coat of arms represents the present and the past. Red and white are the colours of Holstein.[30][31] |
 | Vertical variant. | ||
 | Ostholstein | 30 July 1971 – | A red-white-red horizontal flag with the coat of arms. The coat of arms contains a castle represents Oldenburg while the mitre and the cross represents Eutin (which used to be part of the Prince-bishopric of Lübeck).[32][33] |
 | Pinneberg | 12 May 1986 – | A blue-white-red horizontal flag with the coat of arms. The coat of arms features a nasselblatt represents the counts of Schauenburg and Holstein. The fir tree symbolizes the location of one of the largest nurseries in Germany. Designed by Paul Weber.[34][35] |
 | Plön | 12 May 1975 – | A blue-white-red (which are the colours of Schleswig-Holstein) horizontal flag with the coat of arms. The coat of arms features a nasselblatt represents the counts of Schauenburg and Holstein. The oak leaf represents forests. The ear of grain represents agriculture. The fish represents the district's 80 lakes and the Baltic Sea.[36][37] |
 | Rendsburg-Eckernförde | 29 January 1981 – | A red and yellow diagonal flag with a two blue lions and the yellow triangle (representing Eckernförde and Schleswig) and a nasselblatt on the red triangle (representing Rendsburg and the municipalities that were transferred from Plön and Holstein). The wavy pattern represents the Baltic Sea, the Eider river and the Kiel Canal. Designed by Wilhelm Horst Lippert.[38][39] |
 | Schleswig-Flensburg | 3 October 1977 – | A blue and yellow horizontal flag with a two lions (a blue lion and a yellow lion). The colours were the traditional colours of Schleswig. Designed by Heinz Reinhold.[40][41] |
 | Segeberg | 25 November 1977 – | A red-white-red flag with a cross. The cross represents the introduction of Christianity to Wagria by Vicelinus. The cross is composed of four brick towers representing the churches that Vicelinus built, four leaves of a water lily representing the von Segeberg family and a nasselblatt represents the counts of Schauenburg and Holstein. Designed by George Fink.[42] |
 | Steinburg | 20 July 1957 – | A blue-white-blue flag with the coat of arms. The coat of arms consists of a castle with three coats of arms (representing Wilstermarsch, Holstein and Krempermarsch respectively). Wilstermarsch is represented by an image of Christ the King, Holstein by a nasselblatt and Krempermarsch by a white swan. The three coats of arms are placed on a castle surrounded by a moat. Designed by Max Kahlke.[43][44] |
 | Stormarn | 31 July 1981 – | A red flag with a white swan wearing a crown on its neck. The swan represents its readiness for war.[45][46] |
Historical
| Flag | District | Date | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
 | Altenburger Land | 3 June 1996 – | A red-white-green horizontal tricolour flag with the coat of arms. The rose symbolizes Altenburg, a reborn world and the future. The lion represents the Margravate of Meissen. The yellow and white lion represents Pleissnerland. The nine black and yellow stripes with a green crown represents the House of Wettin. The acorn alludes to the district's status as the birthplace of game of Skat. |
 | Vertical variant. | ||
 | Eichsfeld | 22 March 1995 – | A white-red horizontal bicolour flag with the coat of arms. The eagle alludes to the coat of arms of Frederick William I of Prussia while the wheel represents the Elector of Mainz. |
 | Vertical variant. | ||
 | Eisenach | 2000 – | A blue-white-blue flag with a red cross. |
 | Vertical variant. | ||
 | Eisenach | 5 December 1994 – | A red-white-red flag with a white wheel. |
 | Vertical variant. | ||
 | Gera | 2000 – | A black and yellow flag. |
 | Vertical variant. | ||
 | Gotha | 28 June 1991 – | A white-red horizontal bicolour flag with the coat of arms. |
 | Vertical variant. | ||
 | Greiz | 16 June 1997 – | A yellow-green-yellow flag with the coat of arms. |
 | Vertical variant. | ||
 | Hildburghausen | 16 May 1996 – | A white-red horizontal bicolour flag with the coat of arms. |
 | Vertical variant. |
- Flag of Ilm-Kreis
- Flag of Ilm-Kreis (variant)
- Flag of Jena
- Flag of Jena (variant)
- Flag of Kyffhäuserkreis
- Flag of Kyffhäuserkreis (variant)
- Flag of Nordhausen
- Flag of Nordhausen (variant)
- Flag of Saale-Holzland-Kreis
- Flag of Saale-Holzland-Kreis (variant)
- Flag of Saale-Orla-Kreis
- Flag of Saale-Orla-Kreis (variant)
- Flag of Saalfeld-Rudolstadt
- Flag of Saalfeld-Rudolstadt (variant)
- Flag of Schmalkalden-Meiningen
- Flag of Schmalkalden-Meiningen (variant)
- Flag of Sonneberg
- Flag of Sonneberg (variant)
- Flag of Sömmerda
- Flag of Sömmerda (variant)
- Flag of Suhl
- Flag of Suhl (variant)
- Flag of Unstrut-Hainich-Kreis
- Flag of Unstrut-Hainich-Kreis (variant)
- Flag of Wartburgkreis
- Flag of Wartburgkreis (variant)
- Flag of Weimar
- Flag of Weimar(variant)
- Flag of Weimarer Land
- Flag of Weimarer Land (variant)
References
- ^ John, H.; Köckert, H.; Wüst, G. (1990). Die Kreis- und Gemeindewappen im Regierungsbezirk Karlsruhe. Bremen Angelsachsen Verlag.
- ^ Stadler, Klemens (1964). Deutsche Wappen. Bundesrepublik Deutschland. Bremen Angelsachsen Verlag.
- ^ Walz, Guido (2006). Der Brockhaus Mannheim. 400 Jahre Quadratestadt – Das Lexikon. Bibliographisches Institut & F. A. Brockhaus, Mannheim. ISBN 3-7653-0181-7.
- ^ GABl 560/1983, Government of Zollernalbkreis, 1983
- ^ Bardua, H. (1987). Die Kreis- und Gemeindewappen im Regierungsbezirk Stuttgart. Stuttgart Theiss.
- ^ "Pressestelle des Landkreises Ludwigslust-Parchim". Landkreis Ludwigslust-Parchim.
- ^ "Wappen und Flagge des Landkreises Mecklenburgische Seenplatte". Landkreis Mecklenburgische Seenplatte.
- ^ "Wappen und Logo". Landkreis Nordwestmecklenburg.
- ^ "Hauptsatzung des Landkreises Nordwestmecklenburg" (PDF). Landkreis Nordwestmecklenburg. Archived from the original (PDF) on 7 June 2019.
- ^ "Wappen und Flagge des Landkreises Rostock". Landkreis Rostock.
- ^ "Wappen und Logo". Rostock.
- ^ "Verwendung des Schweriner Stadtwappens". Schwerin.
- ^ "Hauptsatzung der Landeshauptstadt Schwerin". Schwerin.
- ^ "Neufassung der Hauptsatzung für den Landkreis Bad Doberan vom 28. November 2000". Landkreises Bad Doberan. Archived from the original on 7 June 2008.
- ^ "Hauptsatzung der Stadt Chemnitz" (PDF). Chemnitz.
- ^ "Wappen und Logo". Landkreis Leipzig.
- ^ "Flaggen und Wappen der Stadt Leipzig". Stadt Leipzig.
- ^ "Flaggen und Wappen der Stadt Leipzig". Deutsche Gesellschaft für Flaggenkunde.
- ^ "Kreis Dithmarschen". Kommunale Wappenrolle Schleswig-Holstein. State Government of Schleswig-Holstein.
- ^ "Landeskunde". Kreis Dithmarschen.
- ^ "Kreisfreie Stadt Flensburg". Kommunale Wappenrolle Schleswig-Holstein. State Government of Schleswig-Holstein.
- ^ "Stadtportrait". Flensburg.
- ^ Oeding, Andreas; Schwensen, Broder; Sturm, Michael (2009). Flexikon. 725 Aha Erlebnisse aus Flensburg!. Gesellschaft für Stadtgeschichte. ISBN 978-3925856617.
- ^ "Kreis Herzogtum Lauenburg". Kommunale Wappenrolle Schleswig-Holstein. State Government of Schleswig-Holstein.
- ^ "Hauptsatzung des Kreises Herzogtum Lauenburg" (PDF). www.herzogtum-lauenburg.de. Archived from the original (PDF) on 28 November 2015. Retrieved 12 January 2022.
- ^ "Hauptsatzung der Landeshauptstadt Kiel" (PDF). Kiel. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2007-06-28. Retrieved 2021-03-24.
- ^ "Hauptsatzung der Hansestadt Lübeck". Lübeck.
- ^ "Kreis Nordfriesland". Kommunale Wappenrolle Schleswig-Holstein. State Government of Schleswig-Holstein.
- ^ "Das Wappen des Kreises Nordfriesland". Kreis Nordfriesland.
- ^ "Hauptsatzung der Stadt Neumünster" (PDF). Neumünster. Archived from the original (PDF) on 14 January 2016. Retrieved 12 January 2022.
- ^ "Das Wappen der Stadt Neumünster". Neumünster.
- ^ "Kreis Ostholstein". Kommunale Wappenrolle Schleswig-Holstein. State Government of Schleswig-Holstein.
- ^ "Wappen-Geschichte". Kreis Ostholstein.
- ^ "Kreis Pinneberg". Kommunale Wappenrolle Schleswig-Holstein. State Government of Schleswig-Holstein.
- ^ "Wappen und Geschichte". Kreis Pinneberg.
- ^ "Kreis Plön". Kommunale Wappenrolle Schleswig-Holstein. State Government of Schleswig-Holstein.
- ^ "Wappen und Geschichte". Kreis Pinneberg.
- ^ "Kreis Rendsburg-Eckernförde". Kommunale Wappenrolle Schleswig-Holstein. State Government of Schleswig-Holstein.
- ^ "Wappen, Flagge, Siegel". Kreis Rendsburg-Eckernförde.
- ^ "Kreis Schleswig-Flensburg". Kommunale Wappenrolle Schleswig-Holstein. State Government of Schleswig-Holstein.
- ^ "Geschichte des Kreises Schleswig-Flensburg". Kreis Schleswig-Flensburg.
- ^ "Kreis Segeberg". Kommunale Wappenrolle Schleswig-Holstein. State Government of Schleswig-Holstein.
- ^ "Kreis Steinburg". Kommunale Wappenrolle Schleswig-Holstein. State Government of Schleswig-Holstein.
- ^ "Geschichte des Kreises Steinburg". Kreis Steinburg.
- ^ "Kreis Steinburg". Kommunale Wappenrolle Schleswig-Holstein. State Government of Schleswig-Holstein.
- ^ "Wappen und Geschichte". Kreis Stormarn.
- "Wappen und Flaggen des Freistaats Thüringen und seiner Landkreise sowie kreisfreien Städte" (PDF). Landeszentrale für politische Bildung Thüringen.
- Linder, Erich Dieter; Schmidt, Falko (2003-04-23). Der Flaggenkurier Landkreisflaggen Deutschlands: Teil 1: Bayern - heutige Landkreise. Deutsche Gesellschaft für Flaggenkunde.
- Stadler, Klemens; Reinhart, Max (1971). Deutsche Wappen. Bundesrepublik Deutschland: Die Gemeindewappen des Bundeslandes Baden-Württemberg. Bremen Angelsachsen Verlag.
- Staack, Gunnar (1997). Flaggen Deutscher Städte. Deutsche Gesellschaft für Flaggenkunde e.V.
- Neubecker, Ottfried (1952). Deutsche Stadtwappen aus West und Ost. Zigarettenbilder-Zentrale Kosmos: Memmingen.




























































































































































































































































































































































































































