Обезьянка Л'Хоеста
| Обезьяна Л'Хоеста [1] | |
|---|---|
.jpg/440px-L'Hoest's_monkey_(Cercopithecus_lhoesti).jpg) | |
| В непроходимом лесу Бвинди , Уганда | |
| Научная классификация | |
| Домен: | Эукариоты |
| Королевство: | Анималия |
| Тип: | Хордовые |
| Сорт: | Млекопитающие |
| Заказ: | Приматы |
| Подотряд: | Хаплорини |
| Инфрапорядок: | Симиформные |
| Семья: | Церкопитекиды |
| Род: | Аллохроцебус |
| Разновидность: | А. лоэсти |
| Биномиальное имя | |
| Аллохроцебус лхоести П. Склейтер , 1899 | |
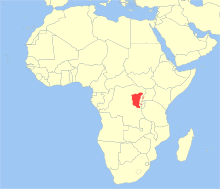 | |
| Географическое распределение | |
_feeding.jpg/440px-L'Hoest's_monkey_(Cercopithecus_lhoesti)_feeding.jpg)
.jpg/440px-Cercopithecus_lhoesti_(L'Hoest's_monkey_-_Colchester_Zoo,_England,_2008).jpg)
Обезьяна Л'Хоеста ( Allochrocebus lhoesti ), также известная как горная обезьяна , является мартышкой, обитающей в верхней восточной части бассейна реки Конго . Они в основном живут в горных лесах небольшими группами, в которых доминируют самки. У них темная шерсть, и их можно отличить по характерной белой бороде.
Таксономия
Первоначально видовое название Cercopithecus lhoesti дал Филипп Латли Склейтер в 1898 году в честь Франсуа Л'Оэста , директора Антверпенского зоопарка . [3]
В настоящее время обезьяна Л'Хоеста классифицируется как представитель рода Allochrocebus . [4] [5] Раньше обезьяна Л'Хоеста включала в себя таксон preussi из региона Гвинейского залива в качестве подвида , [6] но теперь она считается отдельным видом, обезьяной Прейсса ( A. preussi ).
Обезьяна Л'Хоеста ранее была включена в род Cercopithecus . [1] Молекулярные исследования, опубликованные Энтони Тоси в 2003 году, вызвали сомнения относительно классификации обезьяны Л'Хоеста как члена рода Cercopithecus . Исследования показали, что обезьяна Л'Хоеста (вместе с другими в своей видовой группе) более тесно связана с зелеными мартышками рода Chlorocebus и обезьяной патас (род Erythrocebus ), чем с другими мартышками рода Cercopithecus . [7] [8]
Физические характеристики
C. lhoesti has a short, dark brown coat, with a chestnut color across the back and a dark belly. Its cheeks are light gray with a pale moustache. It has a characteristic and prominent white bib,[9] In body length it is 12.5 to 27 inches (32 to 69 cm), with a 19-to-39-inch (48 to 99 cm) tail.[10] The male weighs about 6 kilograms (13 lb), while the smaller female weighs 3.5 kilograms (7.7 lb). Its tail is long and hook-shaped at the end.[11] They are born fully coated and with their eyes open.[10]
Habitat and distribution
L'Hoest's monkey occurs in northeastern Democratic Republic of the Congo, Rwanda, Burundi, and western Uganda.[12] It is a forest monkey, which is typical of the moist and high primary forests. It will occupy a range of different kinds of forested areas, including gallery forest, mature lowland rain forests, wooded savanna at mountain slopes, and forest borders. However, it also will live on cultivated lands. In lowland forests it shows a preference toward areas where the forest is regenerating, while in mountain areas it will frequent the mature, tangled, undergrowth below the broken canopy. One study found this population only above 900 metres (3,000 ft) but another found it as low as 610 metres (2,000 ft). Another mostly observed it from 1,500 to 2,500 metres (4,900 to 8,200 ft).[13]
Behavior
C. lhoesti lives in fairly small groups dominated by females and have only a single male. The females are usually related, while the male stays only a couple of weeks or at most a couple of years. The adult male will make very loud and distinct calls.[11] They are active during the day, mostly during early morning and late afternoon. They sleep in trees in a sitting position, usually either holding branches or each other. When they are alarmed or see they are being observed, they will flee and take shelter in trees, and after become very still.[10][14] They are mostly terrestrial.[6]
Reproduction
L'Hoest's monkey breeds seasonally, with the timing depending on the area. After about a five-month gestation period, a single young will be born. The mother gives birth typically at night and where ever she happens to be at the time. Birth usually occurs at the end of the dry season, which allows lactation when rainfall is highest.[10] She will eat the placenta and lick the baby clean while it hangs on to her belly. The other females in the group will show much interest in the newborn and will try to hold it. After a few months, nursing becomes less frequent, but will continue for about two years when there is another birth. When male offspring reach sexual maturity, they will leave the group.[11] In captivity, they have been known to live for more than 30 years.[15]
Diet
In the wild, L'Hoest's monkey is primarily a herbivore, which will mostly eat fruit, mushrooms, herbs,[16] roots, and leaves. However, it will also occasionally eat eggs, lizards, and small birds.[10]
References
- ^ a b Groves, C. P. (2005). Wilson, D. E.; Reeder, D. M. (eds.). Mammal Species of the World: A Taxonomic and Geographic Reference (3rd ed.). Baltimore: Johns Hopkins University Press. p. 157. ISBN 0-801-88221-4. OCLC 62265494.
- ^ Ukizintambara, T.; Olupot, W.; Hart, J. (2019). "Allochrocebus lhoesti". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2019: e.T4220A92345122. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2019-3.RLTS.T4220A92345122.en. Retrieved 12 November 2021.
- ^ Sclater, P.L. 1898. Reports on the additions to the society's menagerie in June, July, August, September and October 1898 (Plate XLVIII). Proceedings of the general meetings for scientific business of the Zoological Society of London, 585–586. (texte intégral)
- ^ "Allochrocebus". ITIS. Retrieved 2019-07-18.
- ^ "Allochrocebus". Mammal Diversity Database. Retrieved 2019-07-18.
- ^ a b Tappen, N. C. (1960). Problems of Distribution and Adaptation of the African Monkeys. The University of Chicago Press. p. 98.
- ^ Groves, C. (2006). "Taxonomy and Biogeography of the Primates of Western Uganda". In Newton-Fisher, N.; Notman, H.; Paterson, J.; Reynolds, V. (eds.). Primates of Western Uganda (Developments in Primatology: Progress and Prospects). New York, NY: Springer. p. 7. ISBN 978-0-387-32342-8.
- ^ Xing J, Wang H, Zhang Y, et al. (2007). "A mobile element-based evolutionary history of guenons (tribe Cercopithecini)". BMC Biol. 5: 5. doi:10.1186/1741-7007-5-5. PMC 1797000. PMID 17266768.
- ^ Estes, Richard Despard (1992-12-01). The Behavior Guide to African Mammals. University of California Press. p. 660. ISBN 0-520-08085-8.
- ^ a b c d e "L'Hoest's Monkey". Oregon Zoo. Archived from the original on 2006-05-13. Retrieved 2006-09-07.
- ^ a b c "L'Hoest's monkey; Cercopithecus lhoesti". BBC, Science & Nature: Animals. Retrieved 2006-09-07.
- ^ Wilson, Don E.; Reede, DeeAnn M. (2005). Mammal Species of the World: A Taxonomic and Geographic Reference. JHU Press. p. 156. ISBN 0-8018-8221-4.
- ^ Wolfheim, Jaclyn H (1983-08-26). Primates of the World: Distribution, Abundance and Conservation. Routledge (UK). pp. 392–3. ISBN 3-7186-0190-7.
- ^ Setchell, Joanna M; Curtis, Deborah J (2003-09-18). Field and Laboratory Methods in Primatology. Cambridge University Press. p. 34. ISBN 0-521-52628-0.
- ^ "l'Hoest's monkey". Edinburgh Zoo. Archived from the original on 2006-09-25. Retrieved 2006-09-07.
- ^ Moore, Susan A; David, Newsome; Dowlinggrains, Ross Kingston (2002-02-01). Natural Area Tourism. Channel View Publications. p. 39. ISBN 1-873150-24-5.
External links
- ARKive - images and movies of L'Hoest's guenon (Cercopithecus lhoesti)


